Cedar Apple Rust

This fungal disease has a complex life cycle over a two-year period as it rotates between two different hosts. In the spring, the orange gelatinous balls show up on cedar trees. The needles of an Eastern red or ornamental cedar are infected with the fungal disease between June and September by spores that are emitted from apple trees. The following summer, small green galls form on the cedar tree and grow till the following spring, when they mature into brown balls approximately 2” in diameter. The picture above shows what the galls look like in the spring when emitting spores. After spending almost 2 years on cedar trees, the spores emitted from the orange goo will float up to 3 miles till they land on the damp leaves or fruit of an apple or fruit tree, where they form lesions similar to the picture on the left that we see. While the Cedar tree doesn’t appear to have any negative impacts from this disease, the fruit trees can be killed with several years of severe infections. Control can be difficult, but it can be achieved.
The first option is to remove all the hosts near enough to cause an infection, which may or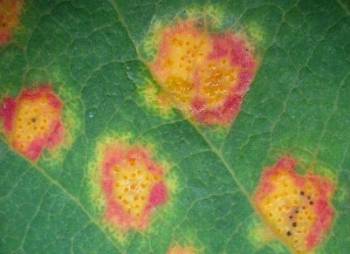 may not be an option depending on your neighbors. If eliminating the hosts is not an option, try to remove the galls you can see from cedar trees as they grow and mature. The final control method is to use a fungicide on the apple trees starting at bloom time and continuing applications every 7 days until the spore spreading from the cedar trees has stopped. You can also spray the cedar trees with fungicide from June to September on 7-14 day intervals, depending on the chemical you are using. Several chemicals, including triforine, propiconazole, myclobutanil, and triadimefon, effectively control rust diseases.
may not be an option depending on your neighbors. If eliminating the hosts is not an option, try to remove the galls you can see from cedar trees as they grow and mature. The final control method is to use a fungicide on the apple trees starting at bloom time and continuing applications every 7 days until the spore spreading from the cedar trees has stopped. You can also spray the cedar trees with fungicide from June to September on 7-14 day intervals, depending on the chemical you are using. Several chemicals, including triforine, propiconazole, myclobutanil, and triadimefon, effectively control rust diseases.

Have questions? Contact our office where our Horticulture Extension Agent will assist you with questions.
Phone: (316) 321-9660
Email: callae@ksu.edu