Spraying Fruit Trees

Fruit trees are very popular; however, they can be prone to several different fungal diseases that can impact the fruit's quality and the tree's overall health. Unlike insecticides, fungal treatments work best when applied as a preventative rather than waiting till you see the disease. Peach leaf curl is one such disease, as is cedar apple rust and apple scab.
Peach leaf curl (photo above) is a disease that causes puckered, swollen, distorted, and reddish-green leaves. The disease ultimately weakens the tree by causing untimely leaf drop when the leaves unfurl in the spring. Luckily, this disease is easy to control with fungicide applications in the spring before bud swell on the tree. The leading fungicide labeled for this disease has the active ingredient chlorothalonil, which is available in several products. Be sure to cover the tree thoroughly for best results. Peach and plum trees should also be sprayed for black knot before the buds swell if that disease has been an issue in the past. The same active ingredient works for both diseases. Sprays for brown rot should begin right as the buds change color and continue according to the label for the season. Products that control that disease include the active ingredients captan or myclobutanil.
Cedar apple rust and apple scab are both common diseases that impact varieties that are not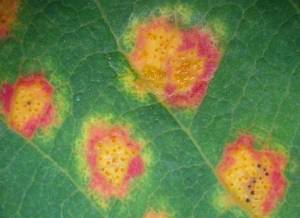 resistant. This is another disease that, if you wait till you see symptoms, you are already too late. Fungicide sprays in April and May are critical to control these diseases. The first treatment should happen when the leaves appear, and additional sprays should be done on a 7 to 10-day schedule through May to protect the developing fruit and leaves. The most effective product available for homeowners is myclobutanil. Apple trees will also need additional insecticide sprays to prevent damage from codling moths. An insecticide should be sprayed with the fungicide spray following petal drop to prevent wormy apples. Do not use any insecticide during the bloom time to protect bees and other pollinators. Several different fruit tree sprays are available on the market. Be sure to read the label before any application and follow all directions.
resistant. This is another disease that, if you wait till you see symptoms, you are already too late. Fungicide sprays in April and May are critical to control these diseases. The first treatment should happen when the leaves appear, and additional sprays should be done on a 7 to 10-day schedule through May to protect the developing fruit and leaves. The most effective product available for homeowners is myclobutanil. Apple trees will also need additional insecticide sprays to prevent damage from codling moths. An insecticide should be sprayed with the fungicide spray following petal drop to prevent wormy apples. Do not use any insecticide during the bloom time to protect bees and other pollinators. Several different fruit tree sprays are available on the market. Be sure to read the label before any application and follow all directions.

Have questions? Contact our office where our Horticulture Extension Agent will assist you with questions.
Phone: (316) 321-9660
Email: callae@ksu.edu